
Why Is It Called a Cleanroom? Cleanroom Tech Explained
- By:Lisa
- 2025-07-31
- 29
Cleanrooms are ultra-pure environments engineered for industries like semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceutical production, and hospital operating theaters, where precise control over airborne particles, temperature, and humidity ensures contamination-free operations. Aluminum profiles and medical automatic doors are pivotal components, offering durability and efficiency in maintaining pristine conditions. This article delves into the origins of cleanrooms, their core technologies, the tailored design of aluminum profiles, and the practical applications of airtight medical doors, providing actionable insights for industry professionals and decision-makers through real-world examples and data.
The Origins and Naming of Cleanrooms

Historical Context
The concept of cleanrooms emerged in the mid-20th century when industries like aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductors grappled with failures caused by microscopic contaminants. For instance, early semiconductor chips short-circuited due to dust, while pharmaceuticals faced contamination risks. In the 1950s, the United States began pioneering dust-free environments, laying the groundwork for cleanroom technology.
In the 1960s, Willis Whitfield revolutionized the field with the invention of the laminar flow cleanroom. By integrating high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and controlled airflow, he elevated cleanliness to unprecedented levels. This breakthrough gave rise to the term "cleanroom," encapsulating its mission of achieving near-perfect purity. The adoption of the ISO 14644-1 standard later solidified "cleanroom" as a globally recognized term.
Why "Cleanroom"?
The term "cleanroom" is straightforward yet powerful, reflecting the goal of creating a contamination-free workspace. Unlike earlier, less consistent terms like "dust-free room" or "purification chamber," "cleanroom" gained traction through ISO standardization, becoming the universal label across pharmaceuticals, electronics, and healthcare.
Core Technologies of Cleanrooms
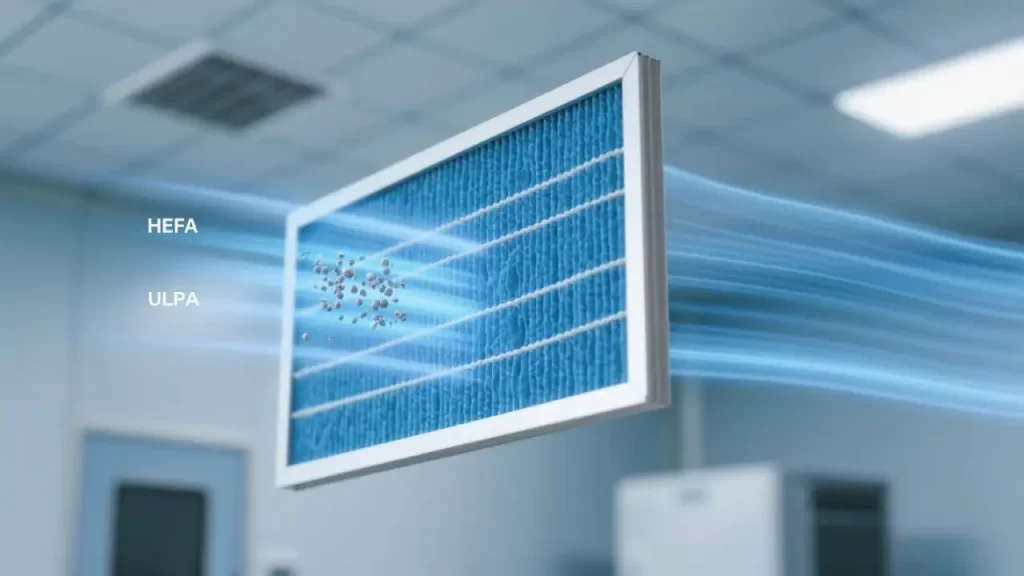
Cleanrooms achieve their pristine conditions through sophisticated environmental control systems. Key components include:
1. Air Filtration and Flow Management
- HEPA Filters: These capture 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns, essential for ISO 5 and higher cleanrooms.
- ULPA Filters: Ultra-low particulate air filters target 0.1-micron particles, ideal for ISO 1 cleanrooms in advanced semiconductor production.
- Airflow Design: Laminar flow delivers unidirectional air to minimize particle settling, while turbulent flow uses mixed airflow for cost-effective applications. HVAC air diffusers, such as linear slot diffusers, ensure uniform air distribution.
Explanation of terms: Laminar flow refers to the flow of air in a single direction, similar to parallel water flow, which is suitable for high-cleanliness environments; turbulent flow refers to the multi-directional mixed flow of air, which is suitable for lower cleanliness requirements and lower costs.
2. Environmental Regulation
Cleanrooms maintain tight control over temperature (typically 68–72°F), humidity (40–60%), and positive pressure to block external contaminants. Ceiling air diffusers optimize airflow, reducing particle accumulation.
3. Operational Protocols
Personnel wear specialized cleanroom suits and pass through air showers to remove surface particles. Materials like antibacterial aluminum profiles and airtight automatic doors are designed for smooth, easy-to-clean surfaces to prevent microbial growth. For example, anodized 6063-T5 aluminum alloy is favored for its corrosion resistance and low maintenance.
Cleanroom Classification Standards
Per ISO 14644-1, cleanrooms are classified from ISO 1 to ISO 9 based on particle counts per cubic meter. Below are common grades and their applications:
| Class | Particles/m³ (≥0.5 μm) | Applications | Aluminum Profile Requirements | Automatic Door Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 1 | ≤10 | Semiconductor Manufacturing | High-precision antibacterial coating | Ultra-high airtightness, rapid operation |
| ISO 5 | ≤3,520 | Pharmaceuticals, Operating Rooms | Corrosion-resistant, easy to clean | Antibacterial, fast response |
| ISO 7 | ≤352,000 | Food Processing, Laboratories | Standard durability | Basic airtightness |
Custom Design of Aluminum Profiles for Cleanrooms
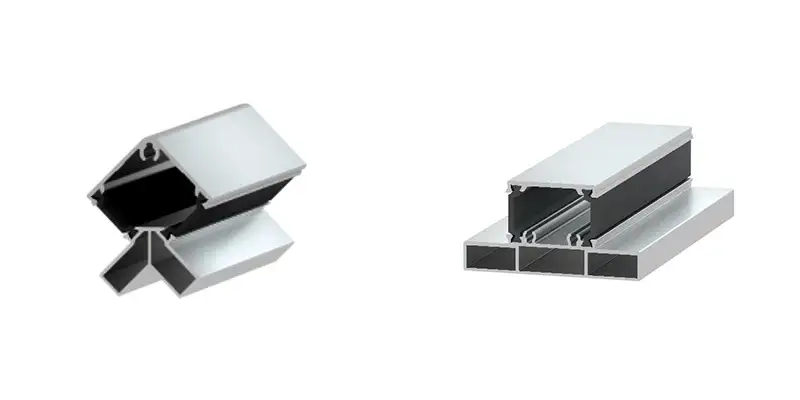

The 6063-T5 aluminum alloy is a go-to material for cleanroom frameworks due to its lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, and versatility. Anodization enhances its antibacterial properties and surface smoothness, cutting maintenance costs. Benefits of modular aluminum profile designs include:
- Rapid Installation: Prefabricated components streamline assembly, reducing construction timelines.
- Seamless Joints: Precision engineering ensures airtight connections, meeting stringent hygiene standards for medical cleanrooms.
- Flexible Customization: Profiles can be tailored for door frames, walls, or structural supports to fit diverse layouts.
Design and Maintenance of Medical Airtight Automatic Doors

Medical airtight automatic doors, made from stainless steel or aluminum alloys, are critical for maintaining cleanroom integrity. Key design features include:
- Superior Airtightness: Silicone seals block external particles, ideal for operating rooms and pharmaceutical plants.
- Swift Operation: Sliding doors open and close in under a second, minimizing air exchange.
- Antibacterial Properties: Stainless steel or antibacterial-coated aluminum reduces microbial risks.
Maintenance Tips:
- Inspect silicone seals monthly, replacing worn parts promptly.
- Clean door surfaces with neutral detergents, avoiding corrosive chemicals.
- Test sensors regularly to ensure smooth operation.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How do I select aluminum profiles for cleanrooms?
Opt for 6063-T5 aluminum with anodized finishes for enhanced durability and antibacterial properties. Verify that suppliers offer ISO-compliant customization. - How should medical cleanroom doors be maintained?
Clean surfaces weekly, check seals and sensors monthly, and conduct annual comprehensive maintenance to ensure airtightness and reliability. - How can cleanroom construction costs be optimized?
Use modular aluminum profiles to cut installation time, select cost-effective airtight doors, and partner with experienced suppliers for optimized designs.
Conclusion
Cleanroom technology, born from mid-20th-century demands for ultra-clean environments, was transformed by Willis Whitfield’s laminar flow innovation and HEPA filters. ISO 14644-1 standards define cleanliness levels, while 6063-T5 aluminum profiles and medical airtight doors enhance efficiency through modular and antibacterial designs. Real-world cases demonstrate that custom profiles can reduce installation time by 25%, and airtight doors lower maintenance costs by 15%. For further insights or supplier recommendations, consult industry resources or connect with experts.
-
 Cleanroom Glass Windows Are The Key to Maintaining a Clean Environment
Cleanroom Glass Windows Are The Key to Maintaining a Clean Environment -
 Top Aluminium Profile Manufacturers in China: Leading the Global Market
Top Aluminium Profile Manufacturers in China: Leading the Global Market -
 The Evolution of Air Tight Sliding Doors
The Evolution of Air Tight Sliding Doors -
 AHU Aluminium Profile: A Comprehensive Guide
AHU Aluminium Profile: A Comprehensive Guide -
 The Importance of Choosing the Right Cleanroom Door in Vietnam
The Importance of Choosing the Right Cleanroom Door in Vietnam -
 The Benefits of Hospital Automatic Doors: Enhancing Efficiency and Safety
The Benefits of Hospital Automatic Doors: Enhancing Efficiency and Safety -
.jpg) The Best Bathroom Door Manufacturers - Unlocking Endless Possibilities!
The Best Bathroom Door Manufacturers - Unlocking Endless Possibilities! -
 Unlock the Possibilities with AJ Manufacturing Doors
Unlock the Possibilities with AJ Manufacturing Doors -
 Make a Statement with Manufactured Home Interior Doors!
Make a Statement with Manufactured Home Interior Doors! -
 what is aluminum profile? Aluminum Profiles for Your Home is the best option
what is aluminum profile? Aluminum Profiles for Your Home is the best option
-
 What to Know About Standard Door Width in Medical Environments
What to Know About Standard Door Width in Medical Environments -
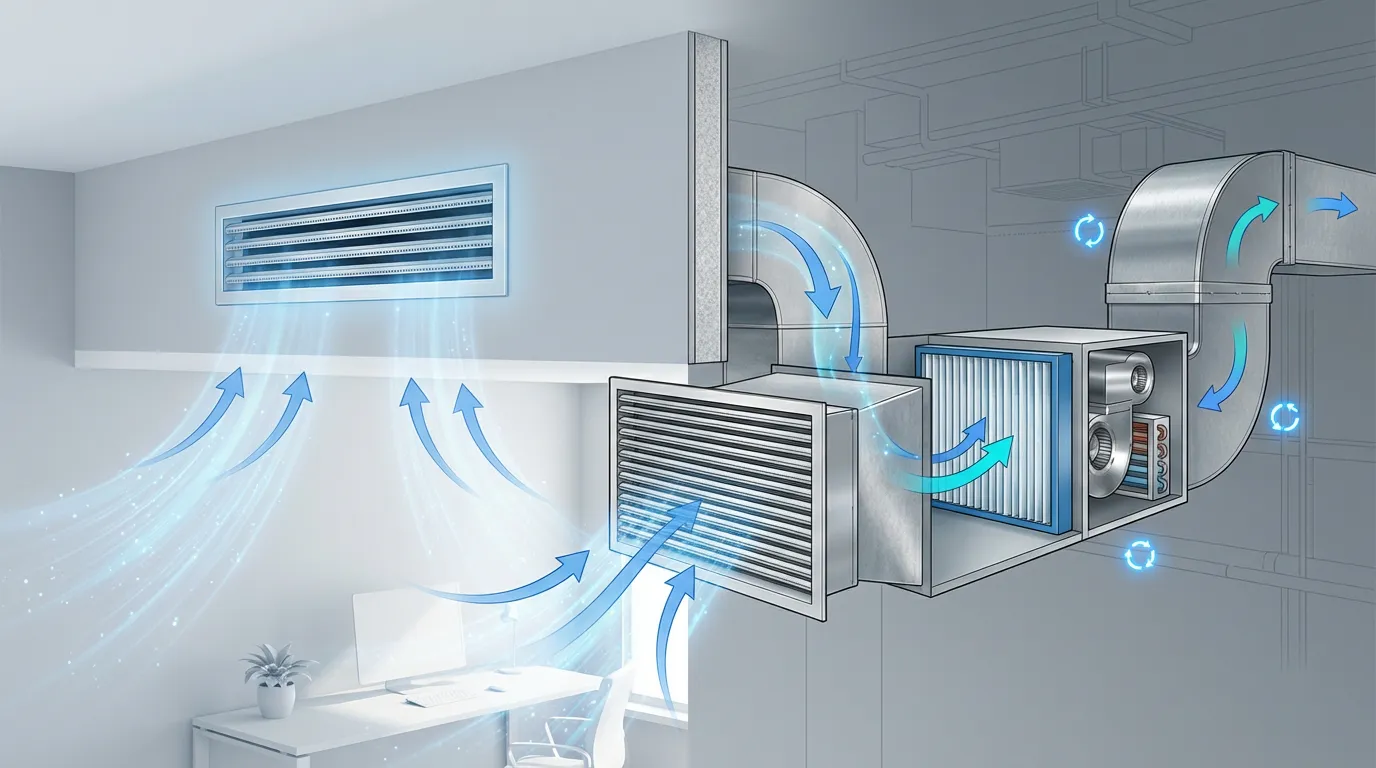 What Is a Return Air Vent and Why Does It Matter in HVAC
What Is a Return Air Vent and Why Does It Matter in HVAC -
 Top Materials for Durable Pharma Clean Room Doors
Top Materials for Durable Pharma Clean Room Doors -
 Hospital Cleanroom Door Design Requirements
Hospital Cleanroom Door Design Requirements -
 Swing Doors vs Standard Doors: Which Is Right for Your Facility
Swing Doors vs Standard Doors: Which Is Right for Your Facility -
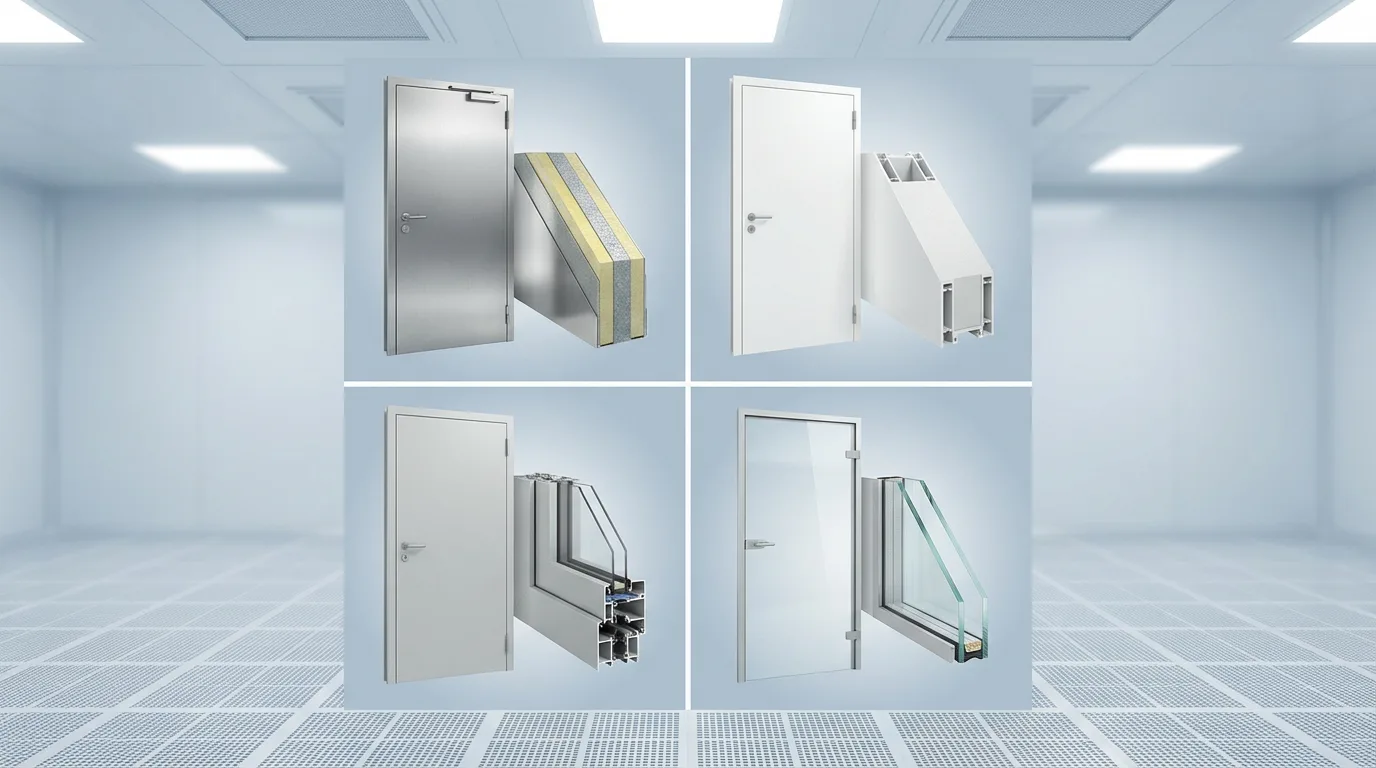 Cleanroom Door Materials Explained: Key Types and Applications
Cleanroom Door Materials Explained: Key Types and Applications -
 How Do Different Vent Grills Impact Medical Cleanrooms
How Do Different Vent Grills Impact Medical Cleanrooms -
 Controlled Environment vs Air Clean Room Differences Explained
Controlled Environment vs Air Clean Room Differences Explained -
 How to Extend the Life of Your Exterior Steel Door
How to Extend the Life of Your Exterior Steel Door -
 What Are the Best Materials for AC Vent Covers
What Are the Best Materials for AC Vent Covers

Guangzhou Yizhong Aluminum Industry Co., Ltd.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.







Speak Your Mind