
What to Know About Standard Door Width in Medical Environments
- By:Lisa
- 2026-01-09
- 29
Medical places need to be exact and safe, especially with door sizes. The standard door width in patient bedrooms, emergency rooms, isolation rooms, and operating rooms is very important. It helps people get in and out easily and follow the rules. Look at the table below to see the newest sizes:
| Room Type | Minimum Clear Door Width | Minimum Clear Door Height |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Bedrooms | 1400mm | 2140mm |
| Existing Patient Rooms | 1200mm | 2040mm |
| Access for Stretchers | 900mm | N/A |
| Access for Hoists | 1000mm | N/A |
Picking the right door size helps workers move patients and tools easily. Hospitals use things like E-ZONG cleanroom doors to meet tough rules and keep everyone safe.
Standard Door Widths by Room
Picking the right door for a medical room is not just about how it looks. It is about keeping people safe and making it easy to move around. Each room in a hospital or clinic needs something different. Let’s see what the standard door width is for each room and how these choices help staff and patients every day.
Hospital Patient Rooms
Hospital patient rooms need doors that are wide enough for beds, wheelchairs, and medical equipment. The Facility Guidelines Institute and National Fire Protection Association say what size is best.
| Door Width | Description |
|---|---|
| 36 inches | This is the usual width for hospital doors. It fits wheelchairs and medical equipment. Two people can walk through at the same time. |
A 36-inch door helps nurses move beds and carts. It also helps patients who use wheelchairs or walkers. Many hospitals pick this size to meet safety and accessibility rules.
E-ZONG cleanroom doors can be made to fit these needs. Their airtight seal keeps patient rooms clean and safe. The company works with hospitals to make sure every door is the right size.
Emergency Rooms
Emergency rooms are busy places. People move fast, and equipment must fit through doors quickly. Healthcare rules say what size doors should be.
- New healthcare buildings need 8-foot wide hallways.
- Ambulatory healthcare occupancies need doors at least 44 inches wide.
- Doors must separate hallways from exam rooms.
A wider door in the emergency room lets stretchers and teams move fast. It also keeps patients safe during emergencies. Hospitals often use doors that are at least 44 inches wide here.
E-ZONG has doors that meet these rules. Their team helps hospitals pick the right size for emergency rooms, so everything fits and works well.
Isolation Rooms
Isolation rooms keep patients and staff safe from germs. The standard door width for these rooms must let people move safely and keep germs out.
| Door Type | Minimum Width |
|---|---|
| Sliding breakaway door | 36 inches |
| Clear door width (if sliding not possible) | 44.5 inches |
| Room Type | Minimum Width |
|---|---|
| Intensive Care Unit (ICU) | 1.2 - 1.5 meters |
A sliding breakaway door with a 36-inch width is common. If sliding doors cannot be used, a clear door width of 44.5 inches is needed. In ICUs, doors are usually 1.2 to 1.5 meters wide. These sizes help staff move beds and equipment while keeping the room sealed.
E-ZONG cleanroom doors use airtight technology to stop germs. Their doors can be made to fit exactly what isolation rooms need, helping with safety and cleanliness.
Operating Rooms
Operating rooms have strict rules for door sizes. The Facility Guidelines Institute and other groups say what size is needed so beds, equipment, and teams can move easily.
| Requirement Type | Minimum Clear Opening Width | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| General healthcare doors | 813 mm (32 in.) | Used for exam rooms, patient rooms, restrooms, and more. |
| Hospital doors for bed movement | 1,054 mm (41.5 in.) | Needed for doors along escape routes in hospitals. |
| Exception for small rooms | 711 mm (28 in.) | For rooms under 6.5 m² (70 sf) that do not need wheelchair access. |
| Exception for resident sleeping units | 711 mm (28 in.) | For sleeping units not required to be wheelchair accessible. |
Most operating rooms use doors with a minimum opening of 41.5 inches. This size lets staff move beds and big equipment quickly. Smaller rooms may use doors as narrow as 28 inches, but only if they do not need wheelchair access.
E-ZONG works with hospitals to design doors that meet these tough rules. Their doors help keep operating rooms clean and easy to get into.
Other Specialized Rooms
Some hospital rooms need special doors. Imaging suites, labs, and cleanrooms often need bigger doors for equipment and to keep things clean.
| Door Type | Width Range |
|---|---|
| Single Slide | 7' to 9' |
| Biparting Slide | 8' to 16' |
| Application | Recommended Use |
|---|---|
| UltraClean | Cleanrooms, labs, pharmaceutical applications |
- Labs
- Waiting areas
- Surgical suites
- Diagnostic imaging areas
- Data and record centers
A single slide door can be 7 to 9 feet wide. Biparting slide doors can be even wider, from 8 to 16 feet. These sizes help staff move big machines and keep the area clean.
E-ZONG helps hospitals pick the right door for each special room. Their team looks at what each space needs and suggests doors that fit both the standard width and the special needs of the room. The process includes making drawings and prototypes quickly, so hospitals get the doors they need fast.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Quality Assurance | E-ZONG checks that every door meets the right rules and standards. |
| Compliance Standards | The doors are made to follow strict industry rules, so users feel safe. |
| Customization Process | E-ZONG works with clients to make custom doors that work better and are more efficient. |
Picking the right standard door width for each room helps hospitals stay safe, clean, and ready for anything. It also makes life easier for staff and patients. Hospitals can work with experts to make sure every door fits and follows all the rules.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Healthcare facilities must follow strict rules for door sizes. These rules help keep patients safe and make spaces easy to use. Hospitals and clinics rely on these standards to plan, build, and upgrade their rooms.
ADA Requirements
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) sets clear rules for door widths in medical buildings. These rules make sure people using wheelchairs or walkers can move around without trouble. The ADA also helps staff move equipment and beds safely.
| Requirement Type | Specification |
|---|---|
| Minimum Clear Width | 32 inches (815 mm) minimum |
| Maximum Clear Width | 48 inches maximum |
| Door Opening Angle | Must open to 90 degrees |
| Maneuvering Clearances | Required for wheelchair access |
A door must open to at least 90 degrees. The clear opening must be at least 32 inches wide. This size lets wheelchairs pass through easily. Hospitals use these rules for patient rooms, exam rooms, and public spaces.
NFPA and FGI Guidelines
Fire safety and patient care depend on following NFPA and FGI guidelines. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and Facility Guidelines Institute (FGI) set standards for door widths and hardware.
- Corridor doors need positive latching hardware to stay closed during a fire.
- Most doors must have a clear opening width of at least 813 mm (32 in.).
- Smaller rooms under 6.5 m² (70 sf) can have doors as narrow as 711 mm (28 in.) if they do not need wheelchair access.
- Doors along escape routes in hospitals must be at least 1,054 mm (41.5 in.) wide to fit beds.
NFPA 101 also says doors must resist smoke passage. The gap between the door and floor should not be more than 1 inch. These rules help protect patients and staff during emergencies.
Local Building Codes
Local building codes add more rules for door widths. These codes can change from city to city. Most new healthcare buildings must meet accessibility standards. Common use spaces like recovery rooms and exam rooms must be accessible.
- Sliding and folding doors must provide at least 32 inches of clear opening width.
- Commercial swing doors usually need a minimum of 32 inches clear opening.
- For double doors, at least one leaf must provide 32 inches of clear opening.
Hospital doors for moving beds must be at least 41-½ inches wide. Openings deeper than 24 inches need a clear opening width of at least 36 inches. No objects can stick out into the required clear opening between the floor and 34 inches above the floor.
E-ZONG designs cleanroom doors to meet or exceed ADA, NFPA, FGI, and local code requirements. Their team helps hospitals choose doors that fit every standard door width needed for compliance and safety.
Why Standard Door Width Matters
Accessibility and Equipment
Medical staff must move patients and equipment fast. Wide doors make this easy. Hospitals use wheelchairs, stretchers, and bariatric beds a lot. If a door is too small, staff have trouble moving these things. Patients feel safer when they can move without problems.
- Doors should be at least 42 inches wide for exam rooms and bathrooms.
- Patient room and procedure area doors work best at 60 inches wide.
- Bi-fold, pocket, and sliding doors help with accessibility.
- Wheelchair access needs a minimum width of 32 inches when open.
- A preferred width of 36 inches allows for easier movement, especially for larger wheelchairs.
Wide doors also help staff move carts and monitors. E-ZONG makes doors that fit these needs. This makes daily work easier for everyone.
Safety and Egress
Safety is most important in emergencies. People need to leave rooms quickly. Hospitals follow rules for door sizes to help people escape fast. The International Building Code and medical guidelines set the smallest and biggest door sizes.
| Regulation | Minimum Width | Maximum Width |
|---|---|---|
| IBC | 32 inches | 48 inches |
| Medical Facilities | 41.5 inches | N/A |
Fire safety rules say doors must be at least 32 inches wide. Some hospital doors need to be 41.5 inches wide for beds and stretchers. Wider doors help people get out faster during fires or other emergencies.
| Regulation | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Minimum clear width for doors in hospitals | 32 inches (810 mm) |
| Existing door width allowance | 34 inches (865 mm) permissible |
| Minimum clear width for corridor doors (if no evacuation by bed, gurney, or wheelchair required) | 28 inches (710 mm) permissible |
Hospitals use these rules to keep everyone safe. Staff and patients can leave fast when every second matters.
Infection Control
Clean rooms stop infections from spreading. Door openings change air quality in operating and isolation rooms. When someone opens a door, air moves between rooms. This can bring in germs and dust.
| Evidence Description | Findings |
|---|---|
| Door openings impact on bacterial counts | Increased bacterial counts in the OR due to air exchange with adjacent spaces, raising the risk of SSIs. |
| Door opening behavior analysis | 23% of door openings were by non-core surgical staff, indicating a need for better communication and design efficiency. |
| Impact of door openings on airborne bacteria | High number of door openings correlates with increased airborne bacteria and viable bacteria on surfaces in the OR. |
| Air quality measurements during surgeries | 13.4 door openings per hour led to a 13% increase in air particle counts, indicating a direct impact on air quality and potential infection risk. |
Hospitals pick doors with airtight seals to lower these risks. E-ZONG has solutions that help keep rooms clean and safe. The right standard door width helps infection control by stopping extra openings and keeping air clean.
Factors Affecting Door Width Choices
Special Equipment Needs
Medical places need doors wide enough for special equipment. Hospital beds and imaging machines need extra space. Bariatric wheelchairs also need more room. Staff must move these things quickly and safely. Teams check the biggest equipment used in each area. They also think about new technology that may need more space later.
- MRI and CT scanners need double or sliding doors.
- Surgical suites need wider doors for carts and monitors.
- Patient lifts and hoists need clear openings.
Picking the right door width helps staff work faster. It keeps patients safe. It also makes cleaning and fixing things easier.
Renovations and Upgrades
Renovating hospitals brings many challenges. Teams must make doors meet new codes and rules. They also need to keep the hospital working during building. Some common problems are:
- Meeting code and accessibility rules
- Finding unexpected floor issues
- Not stopping hospital work
- Balancing design with space needs
Healthcare doors must open at least 32 inches wide. Small rooms not for wheelchairs can have doors as narrow as 28 inches. Doors for beds must be at least 41.5 inches wide. The ADA sets rules for clear space to help people move easily.
Custom Solutions from E-ZONG
Some medical rooms need doors that are not standard sizes. Custom doors help with special needs for width and automation. E-ZONG gives options for these cases.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Tailored Designs | Designs fit what each medical place needs. |
| Unique Width Customization | Double doors can be made to any width needed. |
| Advanced Features | Automated doors and air-tight seals help medical rooms work better. |
| Expertise in Custom Solutions | Many choices make sure doors fit and work well. |
Hospitals and labs get real benefits from custom doors. One drug company had 30% fewer contamination problems. Another hospital made surgical suites safer for patients. These results show how the right door helps with safety and following rules.
Picking the right door width in hospitals is important. It keeps everyone safe and helps workers do their jobs well. Here are some main sizes to remember:
- Patient rooms need doors 36 inches wide.
- Emergency rooms need doors at least 44 inches wide.
- Isolation rooms need doors between 36 and 44.5 inches wide.
- Operating rooms need doors at least 41.5 inches wide.
Hospitals must follow rules like ADA, NFPA, FGI, and local codes. These rules help every hospital project stay safe and legal. If you want more help or special doors, you can check E-ZONG’s cleanroom door page.
FAQ
What is the minimum door width for a hospital patient room?
A hospital patient room door must be at least 36 inches wide. This size lets staff move beds and wheelchairs without trouble. It also helps them bring in medical equipment. The door meets most safety and accessibility rules.
Why do emergency rooms need wider doors?
Emergency rooms need doors that are at least 44 inches wide. These wide doors let stretchers and teams move fast. They help during emergencies and make patient care safer. Wide doors also help doctors and nurses work quickly.
How do door widths affect infection control?
Wide, airtight doors help stop germs from spreading. Fewer door openings mean less air moves between rooms. This lowers the chance of bacteria spreading in places like operating rooms.
Can hospitals customize door widths for special equipment?
Hospitals can get custom door widths for big machines. E-ZONG makes doors for rooms with MRI or CT scanners. These doors help staff move equipment safely and easily.
Do local building codes change door width requirements?
Local building codes can change what door width is needed. Hospitals should check city or state rules before building. Most codes use ADA, NFPA, and FGI rules, but some places have extra rules.
-
 Cleanroom Glass Windows Are The Key to Maintaining a Clean Environment
Cleanroom Glass Windows Are The Key to Maintaining a Clean Environment -
 Top Aluminium Profile Manufacturers in China: Leading the Global Market
Top Aluminium Profile Manufacturers in China: Leading the Global Market -
 The Evolution of Air Tight Sliding Doors
The Evolution of Air Tight Sliding Doors -
 AHU Aluminium Profile: A Comprehensive Guide
AHU Aluminium Profile: A Comprehensive Guide -
 The Importance of Choosing the Right Cleanroom Door in Vietnam
The Importance of Choosing the Right Cleanroom Door in Vietnam -
 The Benefits of Hospital Automatic Doors: Enhancing Efficiency and Safety
The Benefits of Hospital Automatic Doors: Enhancing Efficiency and Safety -
.jpg) The Best Bathroom Door Manufacturers - Unlocking Endless Possibilities!
The Best Bathroom Door Manufacturers - Unlocking Endless Possibilities! -
 Unlock the Possibilities with AJ Manufacturing Doors
Unlock the Possibilities with AJ Manufacturing Doors -
 Make a Statement with Manufactured Home Interior Doors!
Make a Statement with Manufactured Home Interior Doors! -
 what is aluminum profile? Aluminum Profiles for Your Home is the best option
what is aluminum profile? Aluminum Profiles for Your Home is the best option
-
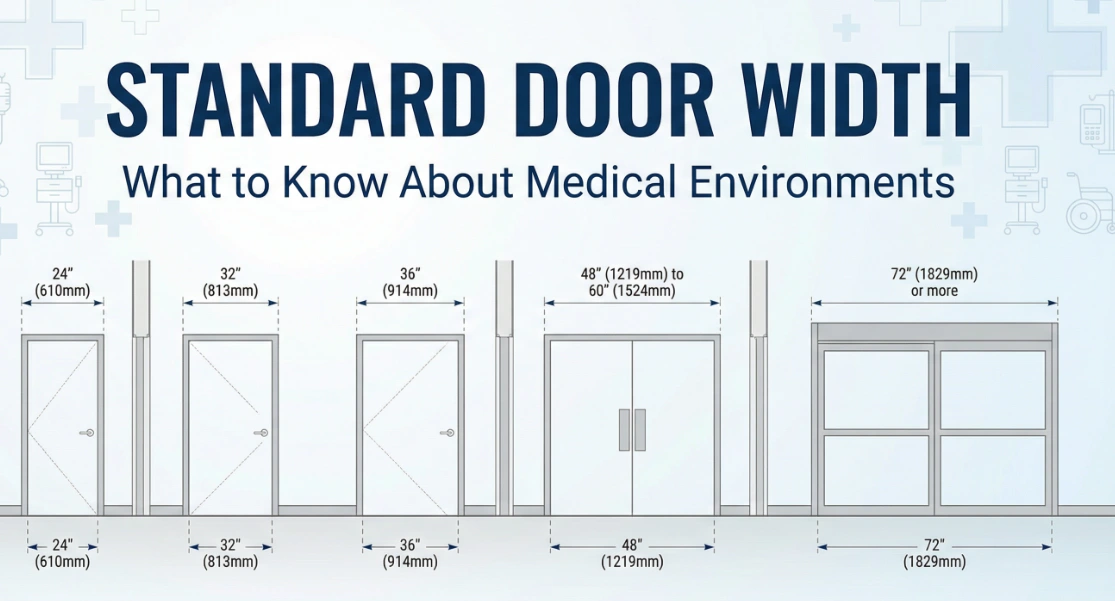 What to Know About Standard Door Width in Medical Environments
What to Know About Standard Door Width in Medical Environments -
 What Is a Return Air Vent and Why Does It Matter in HVAC
What Is a Return Air Vent and Why Does It Matter in HVAC -
 Top Materials for Durable Pharma Clean Room Doors
Top Materials for Durable Pharma Clean Room Doors -
 Hospital Cleanroom Door Design Requirements
Hospital Cleanroom Door Design Requirements -
 Swing Doors vs Standard Doors: Which Is Right for Your Facility
Swing Doors vs Standard Doors: Which Is Right for Your Facility -
 Cleanroom Door Materials Explained: Key Types and Applications
Cleanroom Door Materials Explained: Key Types and Applications -
 How Do Different Vent Grills Impact Medical Cleanrooms
How Do Different Vent Grills Impact Medical Cleanrooms -
 Controlled Environment vs Air Clean Room Differences Explained
Controlled Environment vs Air Clean Room Differences Explained -
 How to Extend the Life of Your Exterior Steel Door
How to Extend the Life of Your Exterior Steel Door -
 What Are the Best Materials for AC Vent Covers
What Are the Best Materials for AC Vent Covers

Guangzhou Yizhong Aluminum Industry Co., Ltd.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.







Speak Your Mind