
Cleanroom Door Materials Explained: Key Types and Applications
- By:Lisa
- 2025-12-18
- 29
Why Cleanroom Door Materials Matter
In controlled environments, doors are not simple architectural elements. In a clean room, doors act as critical control points for contamination, pressure stability, airflow management, and personnel movement. The selection of cleanroom door materials directly affects how well a facility meets cleanliness classifications, complies with regulatory standards, and maintains long-term operational stability.
Cleanroom doors are repeatedly opened and closed throughout daily operations. Each opening introduces risks related to particulate ingress, pressure fluctuation, and airflow disturbance. For engineers, facility planners, and procurement teams, choosing the right cleanroom door material is a critical decision. This is essential across industries like pharmaceutical manufacturing, semiconductor fabrication, biotechnology, medical device production, and food-grade processing.
This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of the materials commonly used in cleanroom doors, how each material performs under cleanroom conditions, and how material choice influences hygiene, sealing performance, cleanroom door airflow, durability, and compliance with cleanroom standards.
Core Functional Requirements for Cleanroom Door Materials
Before looking at specific cleanroom door materials, it is important to understand their key functional requirements. These requirements ensure proper airflow, contamination control, and durability in cleanroom environments:
- Effective contamination control at door interfaces
- Stable cleanroom pressure differential between zones
- Predictable cleanroom door airflow during opening cycles
- Compliance with ISO cleanroom classification requirements
- Integration with cleanroom aluminum profile installation guide and partitions
- Long-term durability under frequent cleaning and disinfection
These criteria form the baseline for material selection in all cleanroom door systems.
Stainless Steel as a Primary Cleanroom Door Material
Stainless steel is a widely used material for cleanroom doors. It is especially common in pharmaceutical cleanrooms and high-grade laboratories.
Why Stainless Steel Is Used in Cleanroom Doors
Stainless steel offers a combination of mechanical strength and hygienic performance that suits controlled environments:
- Non-porous surface structure
- High resistance to chemical disinfectants
- Minimal particle generation during operation
- Compatibility with cleanroom door sealing systems
In clean room applications, stainless steel doors are often specified for areas with strict hygiene requirements, including sterile corridors, airlocks, and gowning rooms.
Stainless Steel Grades Commonly Used
- 304 stainless steel for general cleanroom environments
- 316 stainless steel for corrosive or high-humidity clean rooms
These grades support repeated cleaning cycles without surface degradation, which is essential for maintaining cleanroom compliance over time.
Impact on Airflow and Pressure Control
Stainless steel cleanroom doors are frequently combined with flush-mounted frames and integrated gaskets to reduce leakage paths. Properly installed, they help stabilize cleanroom pressure differential and reduce turbulence caused by door operation.
Aluminum-Based Cleanroom Door Materials
Aluminum is another commonly used material for cleanroom doors. In particular, it is often paired with modular cleanroom panels. It is valued for being lightweight and versatile, making it suitable for various controlled environments.
Advantages of Aluminum in Cleanroom Doors
Aluminum-based cleanroom doors offer:
- Lightweight structure for frequent operation
- Compatibility with modular cleanroom panels
- Reduced load on cleanroom wall systems
- Flexible cleanroom door height customization
Because aluminum is easier to fabricate than stainless steel, it is often used in projects requiring non-standard door sizes or rapid installation.
Surface Treatment and Cleanroom Compatibility
Aluminum doors are typically anodized or powder-coated using cleanroom-safe finishes. These treatments reduce surface porosity and improve resistance to cleaning agents. While aluminum does not match stainless steel in chemical resistance, it performs well in ISO Class 7–8 clean rooms and support areas.
Composite Panel Materials in Cleanroom Doors
Composite materials are increasingly used in cleanroom door systems, especially where insulation and structural stability are required.
Common Composite Structures
Composite cleanroom doors often consist of:
- Metal skins bonded to insulated cores
- Honeycomb or mineral-filled internal structures
- Seamless surface laminates
These structures improve thermal performance while maintaining cleanroom door integrity.
Application Scenarios
Composite doors are frequently selected for:
- Large cleanroom door height openings
- Equipment pass-through doors
- Corridors with temperature control requirements
When properly sealed, composite doors provide excellent airtightness. They also help reduce the overall door weight, making them easier to install and operate in cleanroom environments.
Glass and Vision Panel Integration
Glass is rarely used as a standalone cleanroom door material but is commonly integrated as vision panels.
Cleanroom-Specific Glass Requirements
Glass used in cleanroom doors must meet:
- Flush installation with door surfaces
- Secure bonding to prevent particle traps
- Compatibility with cleanroom door gasket systems
Vision panels improve visibility and safety. When designed properly, they do not compromise cleanroom airflow.
Sealing Systems and Material Interfaces
Material selection alone does not determine cleanroom performance. The interface between materials and sealing systems is equally important.
Gaskets and Door Frames
Cleanroom doors rely on:
- Continuous perimeter gaskets
- Compression sealing mechanisms
- Flush door frame integration
The interaction between cleanroom door materials and sealing components directly affects leakage rates and cleanroom pressure differential.
Airflow Considerations During Door Operation
Cleanroom door airflow behavior is influenced by:
- Door mass and opening speed
- Seal compression consistency
- Door leaf rigidity
Heavier materials like stainless steel naturally reduce vibration. In contrast, lightweight aluminum doors often need added dampening systems.
Cleanroom Door Height, Width, and Structural Stability
Material choice becomes especially important for large-format cleanroom doors.
Structural Demands of Oversized Doors
In clean rooms where equipment movement is frequent, cleanroom door height and width may exceed standard architectural dimensions. Materials must resist:
- Door leaf deformation
- Frame misalignment
- Seal compression loss
Composite and reinforced aluminum systems balance weight and rigidity for oversized doors.
Regulatory and Cleanroom Standard Considerations
Cleanroom door materials must align with applicable standards:
- ISO cleanroom classification
- GMP clean room guidelines
- FDA and EU regulatory expectations
Material traceability, surface finish consistency, and cleanability documentation are often required during cleanroom validation processes.
Material Selection by Cleanroom Application Type
Pharmaceutical Clean Rooms
Stainless steel and composite doors are the leading materials in pharmaceutical cleanrooms, as they best meet the industry's strict hygiene requirements.
Semiconductor Clean Rooms
Aluminum-based doors are common where airflow control and modular integration are prioritized.
Medical and Biotechnology Facilities
A mix of stainless steel, aluminum, and composite materials is used depending on cleanroom zoning and risk level.
Long-Term Performance and Maintenance
Cleanroom door materials must support:
- Repeated cleaning cycles
- Stable seal compression over time
- Resistance to surface degradation (How to Extend the Life of Your Exterior Steel Door)
Material fatigue or surface damage can compromise a cleanroom's airflow and contamination control. This risk must be addressed during the design phase.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cleanroom Door Materials
Selecting cleanroom door materials is not a cosmetic decision. It directly impacts:
- Contamination control
- Airflow stability
- Regulatory compliance
- Operational efficiency
By understanding how stainless steel, aluminum, composite panels, and integrated glass perform within clean room environments, facility planners can make informed decisions aligned with cleanroom classification and long-term performance goals.
Well-chosen cleanroom door materials contribute to stable pressure control, predictable airflow behavior, and reliable contamination prevention across the entire facility.
-
 Cleanroom Glass Windows Are The Key to Maintaining a Clean Environment
Cleanroom Glass Windows Are The Key to Maintaining a Clean Environment -
 Top Aluminium Profile Manufacturers in China: Leading the Global Market
Top Aluminium Profile Manufacturers in China: Leading the Global Market -
 The Evolution of Air Tight Sliding Doors
The Evolution of Air Tight Sliding Doors -
 AHU Aluminium Profile: A Comprehensive Guide
AHU Aluminium Profile: A Comprehensive Guide -
 The Importance of Choosing the Right Cleanroom Door in Vietnam
The Importance of Choosing the Right Cleanroom Door in Vietnam -
 The Benefits of Hospital Automatic Doors: Enhancing Efficiency and Safety
The Benefits of Hospital Automatic Doors: Enhancing Efficiency and Safety -
.jpg) The Best Bathroom Door Manufacturers - Unlocking Endless Possibilities!
The Best Bathroom Door Manufacturers - Unlocking Endless Possibilities! -
 Unlock the Possibilities with AJ Manufacturing Doors
Unlock the Possibilities with AJ Manufacturing Doors -
 Make a Statement with Manufactured Home Interior Doors!
Make a Statement with Manufactured Home Interior Doors! -
 what is aluminum profile? Aluminum Profiles for Your Home is the best option
what is aluminum profile? Aluminum Profiles for Your Home is the best option
-
 What Is a Return Air Vent and Why Does It Matter in HVAC
What Is a Return Air Vent and Why Does It Matter in HVAC -
 Top Materials for Durable Pharma Clean Room Doors
Top Materials for Durable Pharma Clean Room Doors -
 Hospital Cleanroom Door Design Requirements
Hospital Cleanroom Door Design Requirements -
 Swing Doors vs Standard Doors: Which Is Right for Your Facility
Swing Doors vs Standard Doors: Which Is Right for Your Facility -
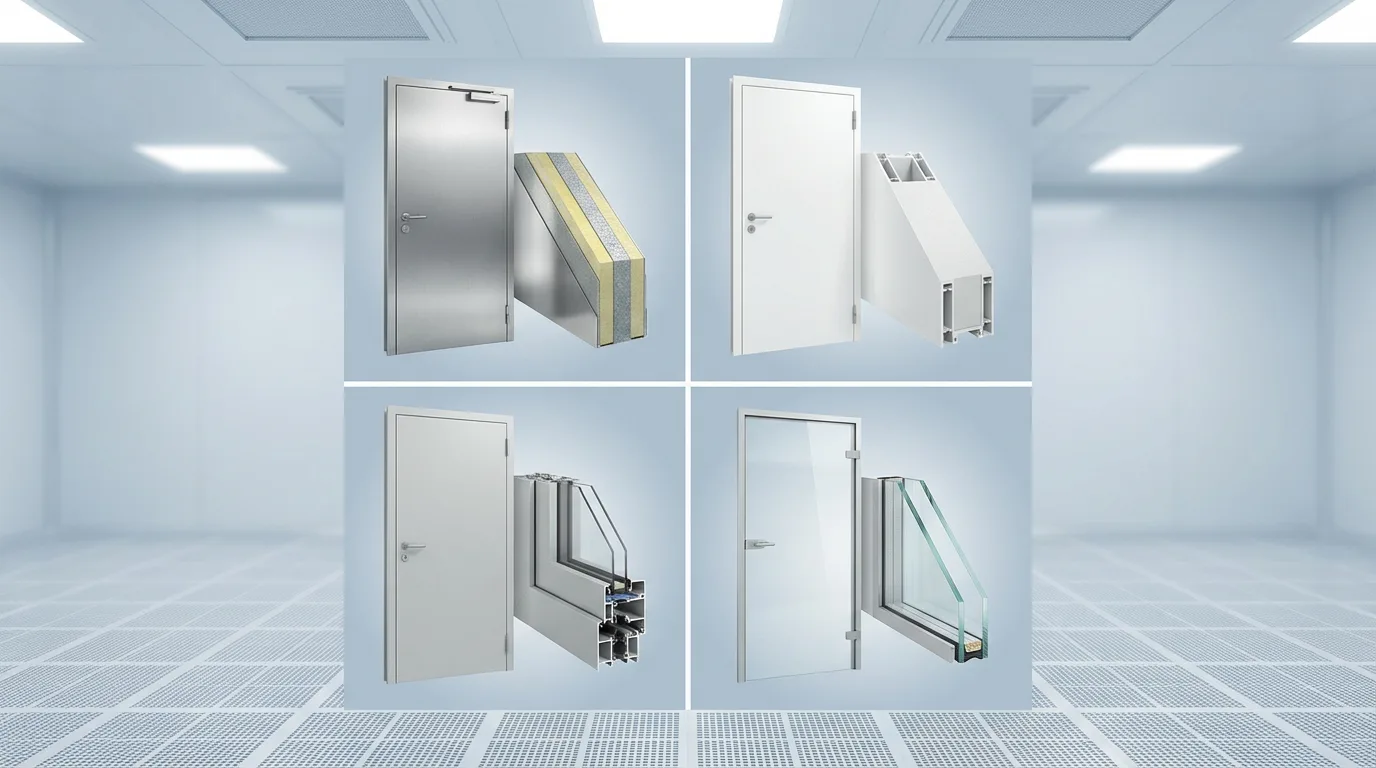 Cleanroom Door Materials Explained: Key Types and Applications
Cleanroom Door Materials Explained: Key Types and Applications -
 How Do Different Vent Grills Impact Medical Cleanrooms
How Do Different Vent Grills Impact Medical Cleanrooms -
 Controlled Environment vs Air Clean Room Differences Explained
Controlled Environment vs Air Clean Room Differences Explained -
 How to Extend the Life of Your Exterior Steel Door
How to Extend the Life of Your Exterior Steel Door -
 What Are the Best Materials for AC Vent Covers
What Are the Best Materials for AC Vent Covers -
 Ceiling Vent Covers Labeled Fire-Rated? Here’s How to Verify
Ceiling Vent Covers Labeled Fire-Rated? Here’s How to Verify

Guangzhou Yizhong Aluminum Industry Co., Ltd.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.







Speak Your Mind