
Why Cleanrooms Are Essential in Pharma & Biotech Manufacturing
- By:Lisa
- 2025-09-29
- 29
In pharmaceutical and biotechnology manufacturing, product safety, efficacy, and consistent quality are non-negotiable. Cleanrooms are not optional facilities—they are a regulatory and operational necessity.
From aseptic filling of injectables to cell therapy production, from viral vector manufacturing to mRNA vaccine formulation, cleanrooms underpin every critical step. Their use is driven by three imperatives: regulatory compliance, product vulnerability, and contamination control.

1. Cleanroom Standards and Classification Systems
A cleanroom is an engineered environment where airborne particles, microorganisms, temperature, humidity, and pressure differentials are tightly controlled to minimize contamination risk.
Globally, cleanroom classifications follow ISO 14644-1 cleanroom standards, which define cleanliness based on the maximum allowable concentration of particles ≥0.5 µm per cubic meter. This system forms the basis of cleanroom ISO classification and ISO cleanroom classifications used worldwide.
In regulated industries, ISO classes map directly to GMP zones:
- ISO 5 cleanroom (Grade A): For high-risk operations like aseptic filling, typically with unidirectional airflow
- ISO 7 cleanroom (Grade C): For sterile compounding and filtration
- ISO 8 cleanroom (Grade D): For non-sterile products with high sensitivity to contamination
This framework guides pharmaceutical cleanroom classification and informs pharmaceutical cleanroom design (FDA, 2004; EU GMP Annex 1, 2022). A compliant GMP clean room must satisfy both ISO particle limits and regional regulatory expectations.
2. The Pharmaceutical Industry’s Non-Negotiable Need for Cleanrooms

2.1 Zero Tolerance in Sterile Manufacturing
Injectables, ophthalmic solutions, and implantables must be free of viable microorganisms and particulates. Even minor contamination can cause sepsis or death. Therefore, aseptic filling must occur within an ISO 5 cleanroom.
For high-risk processes, isolators are increasingly used. An isolator provides a physical barrier between operators and product, maintaining an internal environment equivalent to an ISO 5 cleanroom while minimizing human intervention (EU GMP Annex 1, 2022).
The 2012 U.S. fungal meningitis outbreak—linked to contaminated steroid injections—resulted in 751 infections and 64 deaths (CDC, 2012). This tragedy led regulators to enforce rigorous cleanroom validation services, requiring performance testing per ISO 14644-3:2019, including particle counting, airflow visualization, and recovery time studies.
2.2 Particulate Control and Filtration
Pharmacopoeial standards are strict: the Chinese Pharmacopoeia limits particles ≥10 µm to no more than 25 per mL in large-volume parenterals. Achieving this consistently demands cleanroom HEPA filters, which remove ≥99.97% of particles at 0.3 µm.
Additionally, a pressure differential of at least 10 Pa between adjacent zones prevents airflow reversal and cross-contamination.
In the United States, sterile compounding must comply with USP <797>, which mandates an ISO 5 cleanroom for primary engineering controls. Handling hazardous drugs requires additional containment per USP <800> (USP, 2023).
3. Biotechnology Products: Extreme Environmental Sensitivity

Biologics—including monoclonal antibodies, viral vaccines, and cell and gene therapies—are structurally complex and highly vulnerable to environmental fluctuations.
3.1 Cell Therapy Requires Ultra-Controlled Environments
In cell therapy, living cells serve as the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). Research shows that endotoxin levels above 0.1 EU/mL can significantly inhibit T-cell proliferation (Journal of Immunological Methods, 2018). Therefore, cell expansion must occur in an ISO 5 or ISO 7 cleanroom, supported by rigorous cleanroom environmental monitoring of air, surfaces, and personnel.
3.2 Dual Requirements for Vaccines and Viral Vectors
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) in mRNA vaccines are prone to aggregation if exposed to particles or microbes. Viral vector production (e.g., adenovirus) also requires biosafety level 2 (BSL-2) containment. The World Health Organization (WHO) explicitly requires that bulk vaccine aseptic filling occur in Grade A/B zones—equivalent to ISO 5/7 cleanrooms under ISO 14644-1 cleanroom standards.
4. Regulatory Requirements Are Absolute
Global regulators treat cleanrooms as a prerequisite for GMP compliance:
- The FDA’s Aseptic Processing Guidance (2004) requires continuous environmental monitoring data to prove control
- EU GMP Annex 1 (2022) emphasizes contamination control strategies (CCS) and dynamic monitoring
- China’s Good Manufacturing Practice regulations mandate GMP certification, for which cleanroom validation services are essential
A robust cleanroom environmental monitoring program must include routine testing for airborne particles, viable microorganisms (e.g., settle plates, active air sampling), and surface bioburden. In Grade A zones, the alert limit for airborne viable counts is typically 1 CFU/m³, with an action limit of 5 CFU/m³ (EU GMP Annex 1).
Moreover, pharmaceutical cleanroom design must integrate quality risk management from day one—ensuring logical separation of personnel and material flows. A compliant GMP clean room must also meet specific requirements for pressure cascades, air change rates, and surface finish.
5. How Cleanrooms Directly Ensure Product Quality
5.1 Preventing External Contamination
- Cleanroom HEPA filters block external particulates
- Positive pressure and airlocks prevent ingress of unfiltered air
- Studies show the probability of contamination in uncontrolled environments can be as high as 1 in 1,000, whereas ISO 5 cleanrooms reduce this to below 1 in 1,000,000 (PDA Technical Report No. 13)
5.2 Controlling Internal Risks
Zoned layouts (Grade A/B/C/D), segregated flows, and routine disinfection (e.g., sporicidal agents) minimize cross-contamination—especially critical in multi-product facilities.
5.3 Supporting Validation and Data Integrity
Continuous monitoring data—particle counts, differential pressure logs, microbial results—are essential for process validation (PV) and continued process verification (CPV). This data must meet ALCOA+ criteria (Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate, plus Complete, Consistent, Enduring, and Available) to satisfy regulatory submissions.
5.4 Mitigating Business and Compliance Risk
A single contamination-related recall can cost over $10 million (FDA Recall Data, 2021). While constructing an ISO 5 cleanroom requires significant capital investment, it prevents costly shutdowns, recalls, and legal liabilities—ensuring uninterrupted market access.
-
 Cleanroom Glass Windows Are The Key to Maintaining a Clean Environment
Cleanroom Glass Windows Are The Key to Maintaining a Clean Environment -
 Top Aluminium Profile Manufacturers in China: Leading the Global Market
Top Aluminium Profile Manufacturers in China: Leading the Global Market -
 The Evolution of Air Tight Sliding Doors
The Evolution of Air Tight Sliding Doors -
 AHU Aluminium Profile: A Comprehensive Guide
AHU Aluminium Profile: A Comprehensive Guide -
 The Importance of Choosing the Right Cleanroom Door in Vietnam
The Importance of Choosing the Right Cleanroom Door in Vietnam -
 The Benefits of Hospital Automatic Doors: Enhancing Efficiency and Safety
The Benefits of Hospital Automatic Doors: Enhancing Efficiency and Safety -
.jpg) The Best Bathroom Door Manufacturers - Unlocking Endless Possibilities!
The Best Bathroom Door Manufacturers - Unlocking Endless Possibilities! -
 Unlock the Possibilities with AJ Manufacturing Doors
Unlock the Possibilities with AJ Manufacturing Doors -
 Make a Statement with Manufactured Home Interior Doors!
Make a Statement with Manufactured Home Interior Doors! -
 what is aluminum profile? Aluminum Profiles for Your Home is the best option
what is aluminum profile? Aluminum Profiles for Your Home is the best option
-
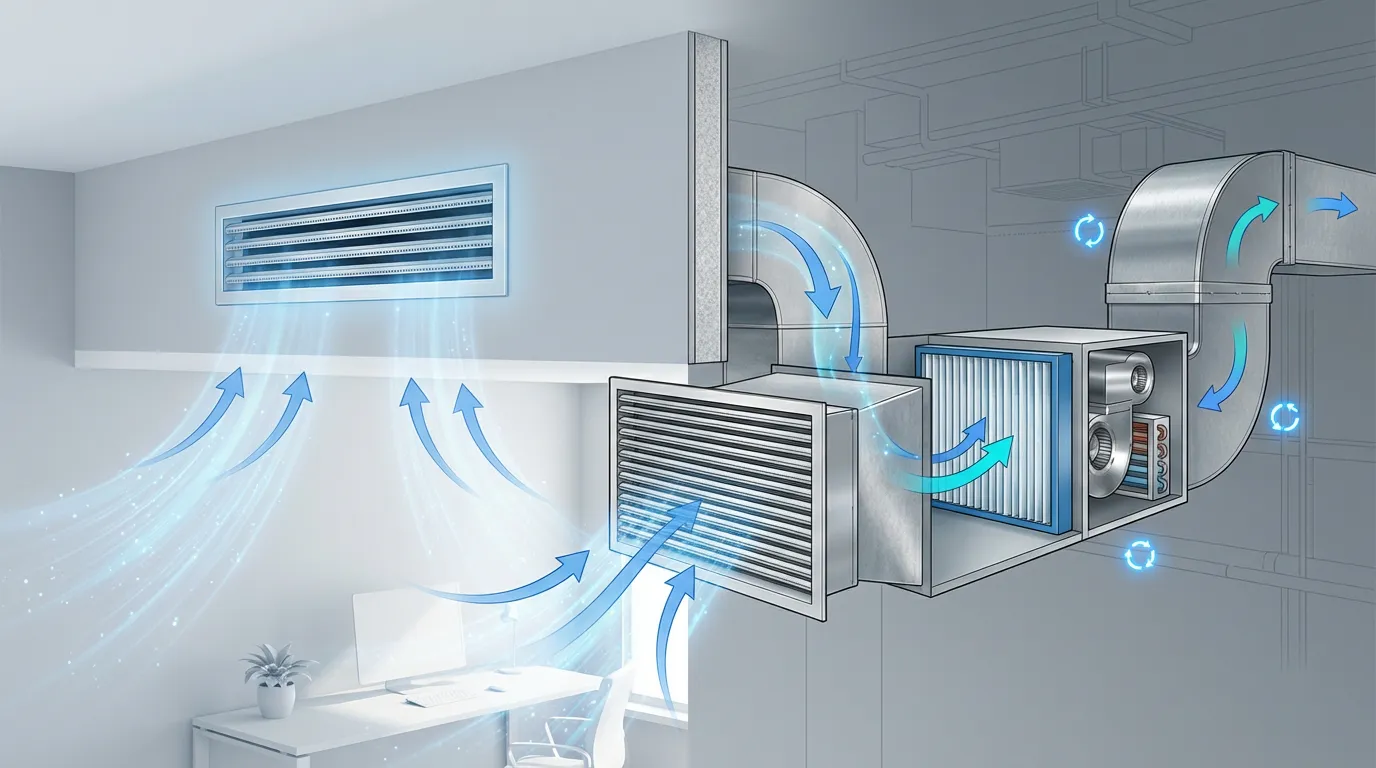 What Is a Return Air Vent and Why Does It Matter in HVAC
What Is a Return Air Vent and Why Does It Matter in HVAC -
 Top Materials for Durable Pharma Clean Room Doors
Top Materials for Durable Pharma Clean Room Doors -
 Hospital Cleanroom Door Design Requirements
Hospital Cleanroom Door Design Requirements -
 Swing Doors vs Standard Doors: Which Is Right for Your Facility
Swing Doors vs Standard Doors: Which Is Right for Your Facility -
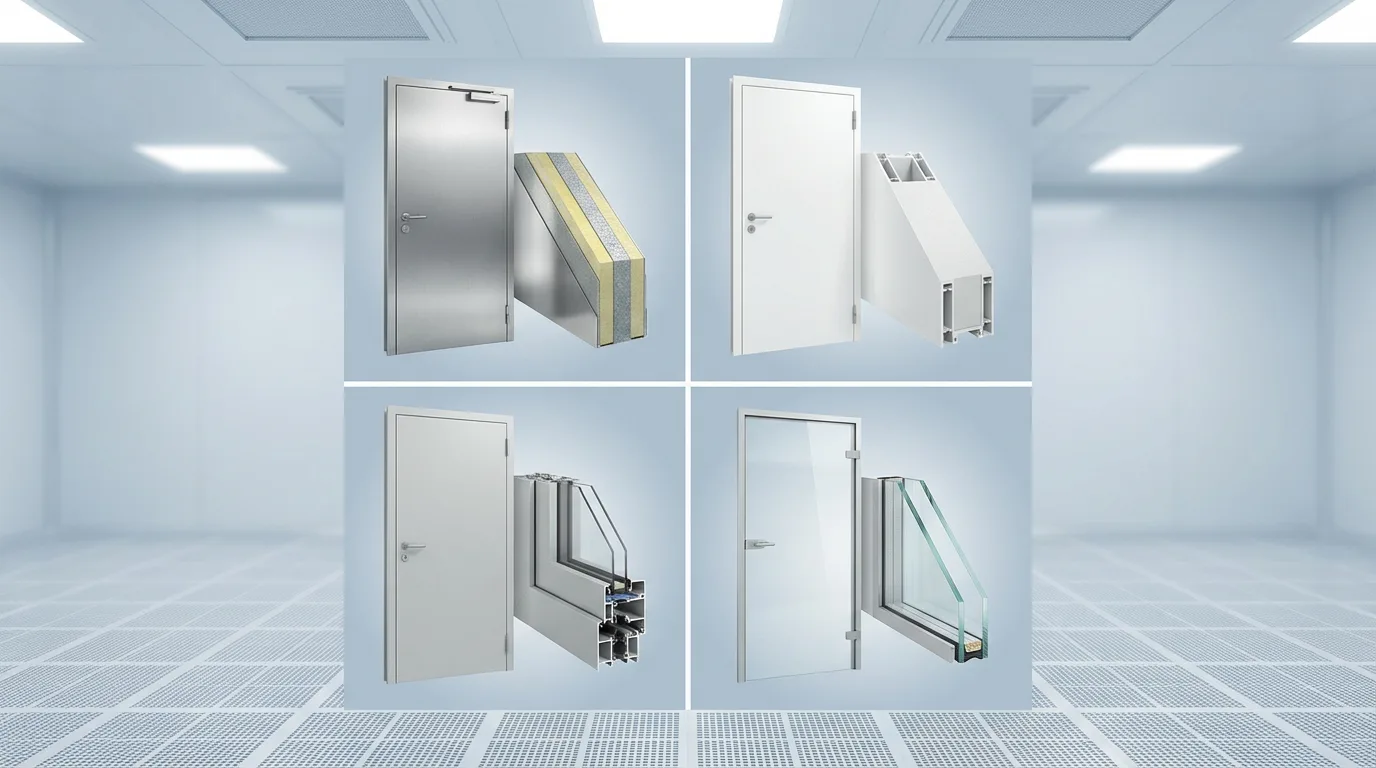 Cleanroom Door Materials Explained: Key Types and Applications
Cleanroom Door Materials Explained: Key Types and Applications -
 How Do Different Vent Grills Impact Medical Cleanrooms
How Do Different Vent Grills Impact Medical Cleanrooms -
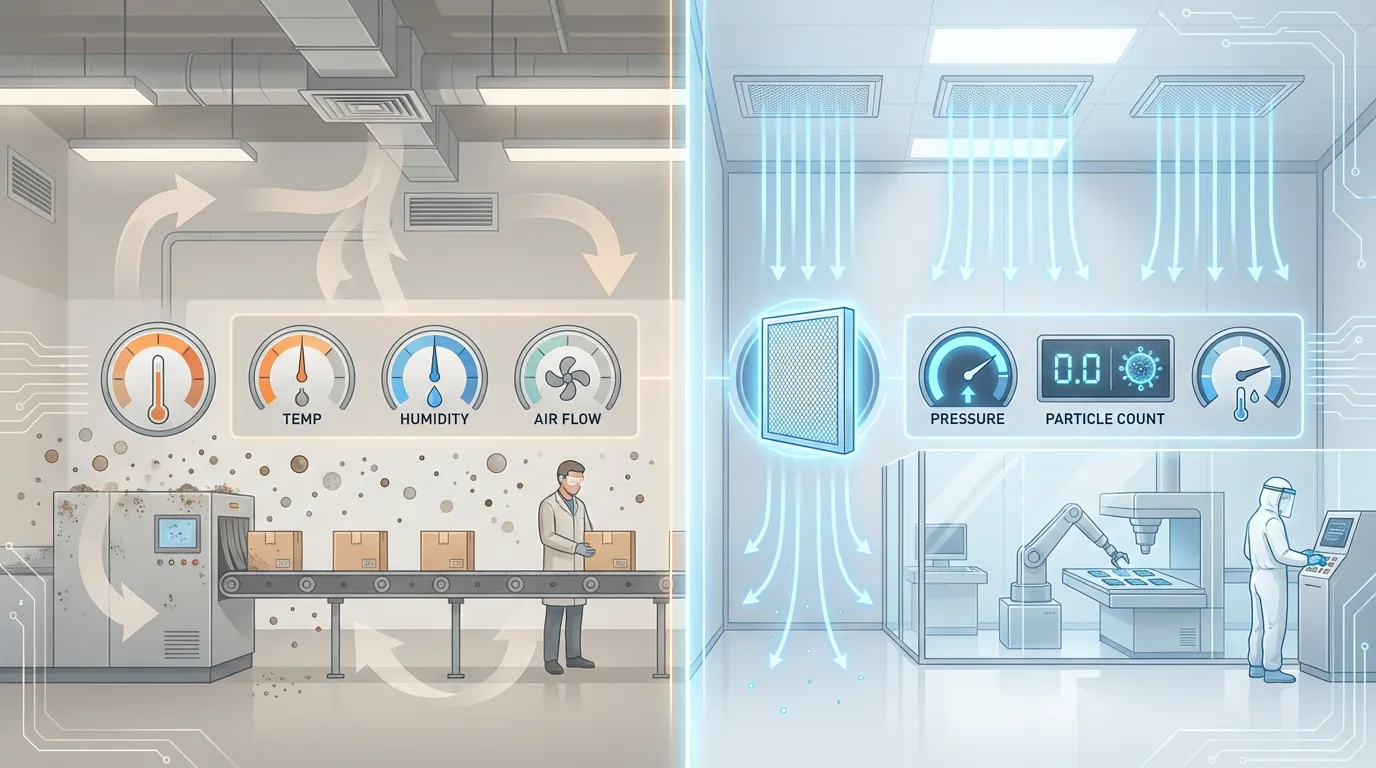 Controlled Environment vs Air Clean Room Differences Explained
Controlled Environment vs Air Clean Room Differences Explained -
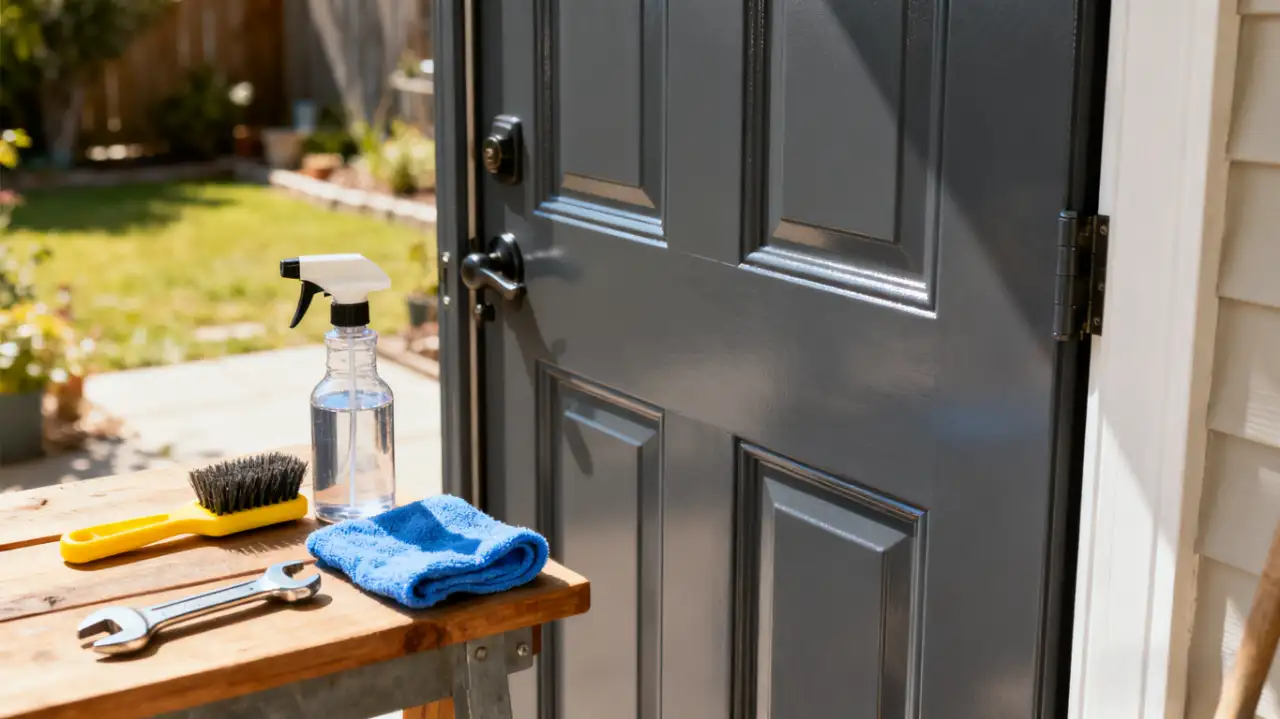 How to Extend the Life of Your Exterior Steel Door
How to Extend the Life of Your Exterior Steel Door -
 What Are the Best Materials for AC Vent Covers
What Are the Best Materials for AC Vent Covers -
 Ceiling Vent Covers Labeled Fire-Rated? Here’s How to Verify
Ceiling Vent Covers Labeled Fire-Rated? Here’s How to Verify

Guangzhou Yizhong Aluminum Industry Co., Ltd.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.
We are always providing our customers with reliable products and considerate services.







Speak Your Mind